Tag: Instruments
-
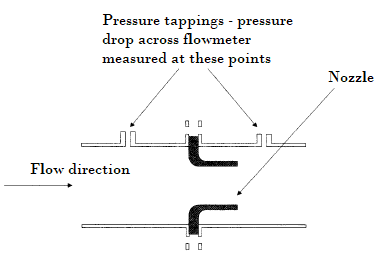
Common Types of Differential Pressure Flowmeters
The term ‘flow’ can generally be applied in three distinct circumstances: Volumetric flow is the commonest and is used to measure the volume of material passing a point in unit time such as m3s-1. It may be indicated at the local temperature and pressure or normalized to some standard conditions using the standard gas law…
-
How to Choose the Perfect Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Among all flow meter types, thermal mass flow meters have become a go-to solution for accurate gas flow measurement in many industries, from manufacturing and chemical processing to environmental monitoring and research laboratories. Their ability to provide precise, repeatable, and direct mass flow readings—without the need for temperature or pressure compensation—makes them highly valuable. But…
-
Distortion Meter vs. Wave Analyzer, How do they Differ?
Though these two instruments may appear similar in their functionality, there are actually subtle differences between them in terms of their functions and operations. The distortion meter is used to measure the total harmonic distortion content in an input waveform whereas the wave analyzer is used to measure relative amplitude of single frequency components in…
-
NAMUR NE 43 for Process Instrumentation Diagnostics
NAMUR NE 43 is a recommendation that seeks to promote the standardization of the signal level for failure information. The objective of NAMUR NE 43 is to set the foundation for proactively employing transmitter failure signals in process instrumentation and control. Using these failure signals, instrument faults are separated from process measurements. Because the faults…
-
China First Eco-Friendly High-Temperature Melt Pressure Transducer Without Mercury Filling
Ziasiot Sensor pioneered China’s first mercury-free, eco-friendly high-temperature melt pressure transducer, which marking a significant technological breakthrough in the melt pressure industry. A Safer Alternative for extrusion melt pressure applications Traditional melt pressure transducers and thermometers have long relied on mercury (Hg) as a filling medium. However, mercury poses severe health and environmental risks due to its toxic…
-
Distortion Meter: Function, Components & Controls
The Function of a Distortion Meter A distortion meter is used to measure the total harmonic distortion content in an input waveform. The rms level of the distortion is usually measured as a percentage of the rms level of the complete waveform. Alternatively, a decibel measurement may be employed. A sine wave input to an…
-
How to Calibrate a DC Ammeter using a Potentiometer
We can calibrate a dc ammeter by connecting it in series with a precision resistor/standard resistor, and accurately measuring the resistor voltage drop. The level of ammeter current is determined by dividing the resistor voltage drop by its resistance value. When the resistor value is known precisely, and the voltage drop is measured by a…
-
Absolute vs. Secondary Instruments
Measuring instruments may be classified as either absolute instruments or secondary instruments. Absolute Instruments This type of instruments gives the value of the measurand in terms of instrument constant and its deflection; this instrument type doesn’t require comparison with any other standard. For instance, the tangent galvanometer gives the value of the current to be…
-
How to Measure Pressure using a U-tube Manometer
There are three categories of pressure measurement, namely absolute pressure, gauge pressure and differential pressure. The absolute pressure is the differences between the pressure at a particular point in a fluid and the absolute zero of pressure, that is, a complete vacuum. When the pressure measuring device measures the difference between the unknown pressure and…
-
Digital Voltmeters: Basic Features, Operation & Applications
The digital voltmeter (DVM) displays measurement of ac or dc voltages as discrete numbers instead of a pointer deflection on a continuous scale as in analog instruments. A digital voltmeter basically consists of an analog-to-digital converter, a set of seven-segment numerical displays and the necessary BCD-to-seven-segment drivers. A digital voltmeter is a versatile and accurate…