Tag: instrumentation and control
-
4–20 mA Is Not Just a Signal — It Is a Safety Decision
Industrial automation continues to evolve rapidly, incorporating digital networks, smart instrumentation, and industrial Ethernet protocols. Despite these advancements, analog current loops—specifically 4–20 mA—remain the most widely deployed communication method for transmitting process variables such as pressure, temperature, level, and flow from field instruments to control systems like PLCs, DCS, and SCADA. Textbooks and engineering training…
-
Thyristor Power Converters: Function, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
Thyristors are semiconductor devices that tend to stay ‘ON’ once turned ON, and tend to stay ‘OFF’ once turned OFF. A momentary event is able to flip these devices into either ON or OFF states, where they will remain that way on their own, even after the cause of the state change is taken away.…
-
Precision Control in Industrial Heating: How Advanced Induction Systems Enhance Efficiency
Modern manufacturing demands smarter heat treatment. Specifically, factories seek greater precision, energy efficiency, and automation. Traditional methods like gas or furnace heating often fall short. They struggle with slow response times, inconsistent results, and high energy waste. So, what is the solution? Advanced induction heating systems answers this call. They offer unparalleled precision control. This…
-
Hydraulic System: Function, Components, Advantages & Drawbacks
Hydraulic systems are built in such way that they are able to move large loads by controlling a high-pressure fluid in distribution lines and pistons with mechanical or electromechanical valves. A typical hydraulic system such as one illustrated below consists of a pump used to deliver high-pressure fluid, a pressure regulator to limit the pressure…
-
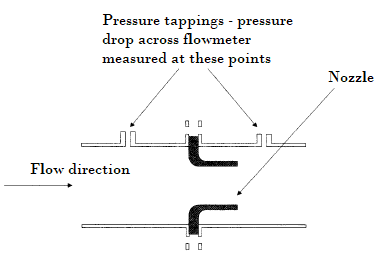
Common Types of Differential Pressure Flowmeters
The term ‘flow’ can generally be applied in three distinct circumstances: Volumetric flow is the commonest and is used to measure the volume of material passing a point in unit time such as m3s-1. It may be indicated at the local temperature and pressure or normalized to some standard conditions using the standard gas law…
-
Analog PID Controller: Basic Features
PID action can be performed using either analog or digital electronic circuits. In this article we look at the fundamental features of an analog PID controller. To help us understand the basic operation of an analog PID controller, let’s consider the block diagram below: In reference to the diagram above, the measured variable from the…
-
PLC Input & Output Modules Circuits
The PLC Input/output modules are control ports either built into the PLC unit or, more commonly, are packaged as separate plug-in modules where each module contains a set of ports. These I/O modules act as interfaces to the outside world. I/O Modules can be broadly classified into two groups: Those that utilize discrete I/O levels…
-
How to Choose the Perfect Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Among all flow meter types, thermal mass flow meters have become a go-to solution for accurate gas flow measurement in many industries, from manufacturing and chemical processing to environmental monitoring and research laboratories. Their ability to provide precise, repeatable, and direct mass flow readings—without the need for temperature or pressure compensation—makes them highly valuable. But…
-
NAMUR NE 43 for Process Instrumentation Diagnostics
NAMUR NE 43 is a recommendation that seeks to promote the standardization of the signal level for failure information. The objective of NAMUR NE 43 is to set the foundation for proactively employing transmitter failure signals in process instrumentation and control. Using these failure signals, instrument faults are separated from process measurements. Because the faults…