Category: Power Systems
-
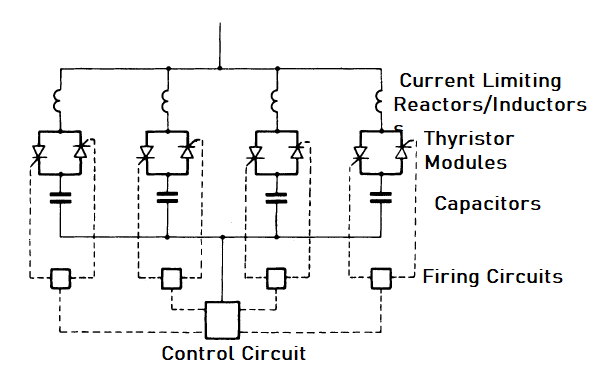
What are Flexible Alternating Current Transmission Systems (FACTS) Controllers?
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) can be described as AC transmission systems incorporating power electronic-based controllers and other static controllers to boost controllability and increase power transfer capability. FACTS equipment that provides control of one or more of the parameters of an electrical network is often referred to as a FACTS controller. FACTS devices may…
-
The Connection of Green Energy Generation Plants to Power Systems: Key Factors to Consider
To prevent negative effects on the operation of the power system and equipment, a number of factors must be considered when connecting green energy generation plants to these systems. The following should be factored in: With the increased development of green energy generation plants, special aspects need to be considered such as the use of…
-
Causes of Power System Disturbances & Corrective Measures
Even though most protective system designs are built around individual components, system-wide disturbances in power systems are rather a frequent occurrence and a challenging issue for electric utility companies. When major disturbances occur in power systems, it is imperative to implement coordinated protection and control actions to stop the system degradation, restore the normal state…
-
Sources of Power Quality Problems
Power quality may be affected by a number of issues. Our discussion in this article focuses on various devices and events that lead to problems in power quality. The common sources of power quality problems include: Power Electronic Devices Power electronic devices cause power quality disturbances and they are also susceptible to them. Variable speed…
-
Common Terms Used When Describing Power Quality Problems
Power quality has become an important issue to electricity consumers at all levels of consumption. This has especially been intensified by the common use of sensitive equipment and non-linear loads in both industrial and the domestic environs. In this article we look at some of the common terms typically used when describing power quality problems.…
-
AC to AC Power Converters with Intermediate DC Link: Types, Features & Applications
This category of AC drives that is often referred to as “Variable Frequency Inverters” is one of the most extensively used drives in industrial motor control applications. Generally, the concept of these inverter drives can be summarized into three parts: We have two main classifications of these AC drives that are based on the aforementioned…
-
Vacuum Circuit Breakers: Features, Operation & Applications
In vacuum circuit breakers, vacuum typically at pressures ranging from 10-9 to 10-6 bar is used as the quenching medium. At such pressures, high dielectric strength can be achieved. The contact separation needed at such low pressures is only 0-20 mm and low energy mechanisms may be employed to operate the contacts through expendables bellows.…
-
DC to DC Power Converters: Function, Types, Operation & Applications
DC to DC power converters also referred to as choppers provide the means to change one DC voltage to another. Normally the conversion is to a lower voltage however, we also have step-up converters. DC to DC power converters are fed from a DC supply usually comprising an uncontrolled AC to DC converter or alternatively…
-
Equipment Grounding vs. System Grounding
Grounding or earthing an electrical system is the process of connecting all metalwork/frame of electrical equipment i.e. the non-current carrying part or some electrical component of the system such as the neutral point in a star-connected system, one conductor of the secondary of a transformer, and so forth to the main body of earth. An…
-
Switchgear Terminology & IEC Standards
Switchgear generally refers to the switching devices and their combinations, with the related control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment. The switchgear equipment basic purpose is switching and interrupting currents either under normal or abnormal operating conditions. Modern power systems, power lines and other apparatus operate at high voltages and carry large currents. When a short…