Author: John Mulindi
-
Power Amplifiers: Function, Classes & Applications
An amplifier is an electronic device that is used to enhance the strength of a signal in terms of voltage, current, or power. It receives a weak electrical signal and produces stronger signal at the output by using an external power source. Small-signal amplifiers are generally referred to as ‘voltage amplifiers’ as they convert a…
-
Thyristor Power Converters: Function, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
Thyristors are semiconductor devices that tend to stay ‘ON’ once turned ON, and tend to stay ‘OFF’ once turned OFF. A momentary event is able to flip these devices into either ON or OFF states, where they will remain that way on their own, even after the cause of the state change is taken away.…
-
Hydraulic System: Function, Components, Advantages & Drawbacks
Hydraulic systems are built in such way that they are able to move large loads by controlling a high-pressure fluid in distribution lines and pistons with mechanical or electromechanical valves. A typical hydraulic system such as one illustrated below consists of a pump used to deliver high-pressure fluid, a pressure regulator to limit the pressure…
-
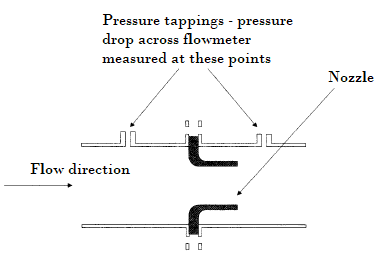
Common Types of Differential Pressure Flowmeters
The term ‘flow’ can generally be applied in three distinct circumstances: Volumetric flow is the commonest and is used to measure the volume of material passing a point in unit time such as m3s-1. It may be indicated at the local temperature and pressure or normalized to some standard conditions using the standard gas law…
-
Analog PID Controller: Basic Features
PID action can be performed using either analog or digital electronic circuits. In this article we look at the fundamental features of an analog PID controller. To help us understand the basic operation of an analog PID controller, let’s consider the block diagram below: In reference to the diagram above, the measured variable from the…
-
PLC Input & Output Modules Circuits
The PLC Input/output modules are control ports either built into the PLC unit or, more commonly, are packaged as separate plug-in modules where each module contains a set of ports. These I/O modules act as interfaces to the outside world. I/O Modules can be broadly classified into two groups: Those that utilize discrete I/O levels…
-
Disaster Recovery in Cloud Hosting: Lessons from Real Downtime Events
It is easy to believe that cloud hosting is bulletproof. This belief is dangerous, as even the best cloud infrastructure fails sometimes. Outages take place in the form of: natural disasters, power failures, cyberattacks, and plain old human mistakes. They all can bring your site or service down. When cloud providers experience downtime, the world…
-
Maintenance Tips for Power Transformers
Maintenance is a routine and recurring activity of keeping a particular equipment or facility at its normal operating condition so that it can deliver its expected performance or service without causing any loss of time on account of accidental damage or breakdown. In other words, maintenance can be described as measures adopted to ensure that…
-
How to Choose the Perfect Thermal Mass Flow Meter
Among all flow meter types, thermal mass flow meters have become a go-to solution for accurate gas flow measurement in many industries, from manufacturing and chemical processing to environmental monitoring and research laboratories. Their ability to provide precise, repeatable, and direct mass flow readings—without the need for temperature or pressure compensation—makes them highly valuable. But…
-
Tube & Tube Fittings – Instrument Tubing Connections
Tube is a hollow structure that is designed to provide an enclosed pathway for fluids to flow just in the same way as the pipe. Tubes are manufactured from rolled or extruded metal however plastic is a common tube material for many industrial applications. In this article we discuss some of the common methods for…