A three-position control is akin to two-point control, except that in this case, the controller has three states, such as forward-off-reverse, (or up-off-down, hot-off-cold, etc.). This is a control strategy that is usually applied in a system that has no specific self-seeking rest state.
To help us demonstrate this control strategy, take a case of a floating oil drilling platform that needs to stay over the wellhead on the ocean bottom as illustrated in Figure 1.0 below. The platform must not drift more than 5 feet away from the center or the pipe may break. Two motors, A and B, are used to keep the platform centered on the east-west axis (the north-south axis would be handled with other motors). If the platform drifts more than 5 feet east, motor A comes ON and drives it back towards the center. Motor B will come ON if the platform drifts more than 5 feet west.
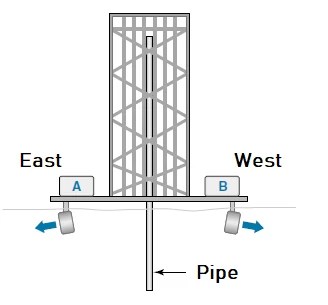
Figure 1.1 below illustrates the platform’s east-west movement. Note that the controlled variable (platform position) will tend to oscillate back and forth across the center because the motor size selected was based on worst-case conditions i.e. strong winds. In calm weather, a brief ON period of motor A may give the platform enough momentum to drift completely across the dead zone, only to be pushed back by motor B.
In actual fact, if the system is not designed accurately, the back and forth oscillations could get bigger and bigger, in which case the system would have gone unstable.
On the other hand, if the wind is too strong for the motor, the platform will be driven outside the 5 feet limit, and the pipe will break.
Related articles:
Image source: Pexels Smart homes are no longer futuristic. They are already here, changing how…
Thyristors are semiconductor devices that tend to stay ‘ON’ once turned ON, and tend to…
Image source: Freepik Introduction: The Evolution of Connectivity Telecommunications have come a long way since…
Modern manufacturing demands smarter heat treatment. Specifically, factories seek greater precision, energy efficiency, and automation.…
An Expert’s Guide to EV Load Management and NEC Compliance Smart EV charging control architectures…
Frequent power failures due to severe storms, aging grid infrastructure, and other unpredictable natural disasters…